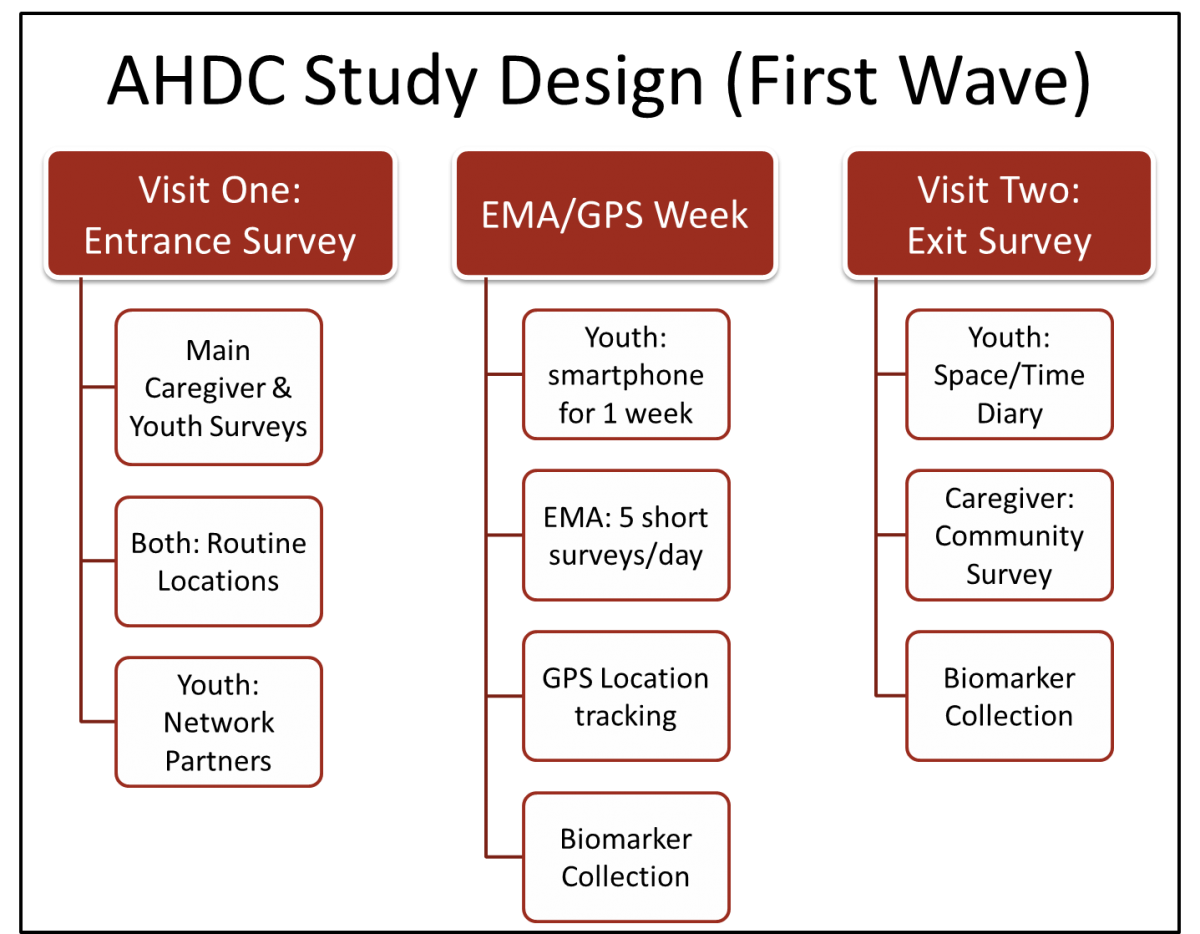
ADHC - Study Design
The AHDC project offers a number of advances over prior data collections focused on youth development.
First, AHDC will collect data on a comprehensive contexts including family and the household, residential, school, social network, and other formal and informal “activity space” contexts (e.g., churches, recreation centers, businesses, and “hang out” locations).
Second, we will use smartphone-based Ecological Momentary Assessment (EMA) to collect real-time data over a seven day period on behavioral settings, including social network partner presence, adult supervision, activities, mood/affect, and behaviors. The smartphones also collects, stores, and facilitates delivery of GPS data tracking the travel path of the youth.
We developed an innovative software application for collecting continuous space/time data over 4 of the 7 days covered by the EMA week. The application inputs the youths GPS and EMA data for each selected day, aiding recall of locations, activities, network partners and behaviors over the course of the day.
Third, we will independently collect Community Survey data on the social climates of neighborhoods and routine activity spaces of Franklin County residents. In combination with a variety of additional administrative data resources, the Community Survey data will allow us to link detailed information on the spaces to which youth are exposed with other survey and EMA data on their characteristics and life experiences.
Biomeasure Data Collection
Finally, we are also collecting biomeasure data to study stress & immune function. We received an R21 award from NIH (PI: Ford) for the collection of cortisol samples, including both nightly saliva for one week and one hair sample. The first aim is to assess the feasibility of nightly collection of cortisol with a subsample of 500 youth from the AHDC study during Wave 1. The second aim is to examine associations between (a) cortisol biomarkers, (b) immune function biomarkers associated with chronic stress (Epstein-Barr virus DNA [EBV DNA] via 1 saliva sample) and (c) linked secondary data from the main AHDC study of adolescent risk behavior and stress exposures.